Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a hot topic today because it powers many smart applications in our everyday life. From smartphones that recognize your face to online services that suggest movies or answer your questions, AI is making technology more intelligent and helpful. Why is AI important? It is changing how we live and work, and knowing about AI can help you in many fields and future careers.
Imagine AI as a helpful robot friend or a study partner. Think about how you learn new things: at first you read examples and practice, and then you get better at solving problems. AI is similar. We teach computers by giving them lots of examples (data) so they can learn patterns. For example, if we show many pictures of cats and dogs to a computer and tell it which is which, it will eventually learn to distinguish cats from dogs on its own. In that sense, AI is like a student that learns from experience and helps us do tasks more easily.
Basic Definition
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the field of technology where computers are made to think and learn in a simple way. In other words, AI lets machines do tasks that usually require human intelligence. These tasks include things like understanding speech, recognizing pictures, making decisions, or playing games.
To break this down in daily life, think about how we learn. A child learns to identify animals by looking at pictures and hearing names. AI works similarly: we give the computer a lot of information or examples (like pictures or words) and it learns from them. For example, when you talk to your smartphone and it understands you, that is AI (speech recognition). When you get a recommendation for a movie on your favorite app, that is AI (smart suggestions). These are simple examples of AI in action.
In very simple terms:
- Artificial means “made by humans, not natural.”
- Intelligence means “the ability to think, learn, and make decisions.”
So, artificial intelligence means machines being able to think and learn a little bit like a human does.
Core Concepts
Human vs. Machine Intelligence
- Human intelligence refers to the brain power that helps people think, learn, and understand. Machine intelligence (AI) means computers doing similar tasks. Computers do not have brains; they follow programs and instructions. AI tries to make computers perform tasks that need thinking, like solving puzzles or understanding speech.
- Humans learn by experience (like reading and practicing), while machines learn from data that we provide. Both can improve over time, but machines do it by analyzing information with algorithms.
Data: Fuel for AI
- Data is information. It can be numbers, pictures, text, or sounds. AI systems need data to learn. For example, many photos of cats and dogs are data for training an AI to recognize pets.
- Just like a student needs textbooks and exercises, an AI needs lots of data. The more good examples it has, the better it learns patterns and makes predictions.
Machine Learning: Teaching Computers
- Machine Learning (ML) is a way of teaching computers by example. Instead of writing fixed rules for every task, we let the computer look at data and learn the rules itself.
- Think of ML as giving a computer many examples with answers, and it figures out the pattern. For example, to teach it to recognize spam email, we give it many spam messages and many normal messages. The computer analyzes them and learns how to spot spam by itself.
- There are different types of ML:
- Supervised Learning: We give the computer labeled examples (input-output pairs), and it learns the mapping.
- Unsupervised Learning: The computer looks at data without explicit labels and tries to find hidden patterns or groups.
- Reinforcement Learning: The computer learns by trying actions and receiving feedback (like rewards or penalties), similar to learning by trial and error.
Algorithms and Models
- An algorithm is a step-by-step recipe or set of rules that the computer follows. In AI, algorithms process data to learn patterns.
- When an AI algorithm learns from data, it creates a model. A model is the final result of learning, like a formula or decision tool the computer uses.
- For example, if the task is to predict housing prices, the algorithm might generate a model (like a mathematical formula) based on past data of house prices. Then, given a new house, the model predicts its price.
- Once a model is created (trained), we use it by feeding new data into it. The model then gives an output (like a decision or prediction).
Types of AI
- Narrow AI (Weak AI): AI systems that are designed for a specific task. For example, a voice assistant, a recommendation engine, or a self-driving car’s vision system are all narrow AIs. They are good at their one task but cannot do everything.
- General AI (Strong AI): A hypothetical computer that has intelligence at human level across any task. This does not exist yet. General AI would be able to reason, learn, and perform any intellectual task a human can, but we have not achieved this.
- Currently, all real AI systems are forms of narrow AI. They only learn specific tasks from data, such as identifying images, translating text, or playing a game.
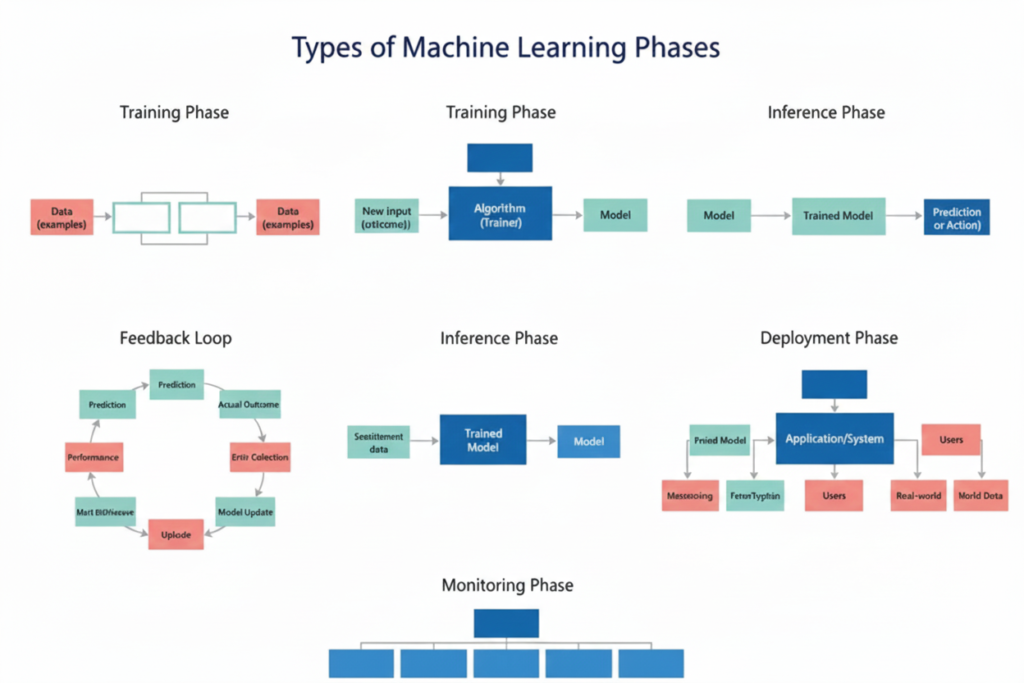
Visual Explanation
AI systems can be viewed in steps. The following ASCII diagram shows a simple view of the training and usage phases of an AI model:
Real-Life Examples
- Smartphones and Voice Assistants: When you ask your phone a question out loud (for example, ‘What’s the weather?’), AI is at work understanding your speech and answering.
- Online Searches: Search engines use AI to predict what you are looking for and show relevant results quickly.
- Media Recommendations: Streaming services and apps use AI to suggest movies, videos, or songs you might like based on your preferences.
- Social Media Feeds: AI decides which posts and ads you see on social media, aiming to show things you might be interested in.
- Email Filters: AI helps sort your emails by moving spam or junk messages out of your inbox automatically.
- Navigation Apps: GPS apps use AI to find the fastest routes and to predict traffic jams in real time.
- Photo Apps: Your phone’s camera can recognize faces and apply filters or suggestions using AI.
- Language Translation: Some online services use AI to convert text from one language to another.
- Online Customer Support: Chatbots on websites can answer customer questions instantly by using AI to understand and respond to messages.
- Everyday Appliances: Some robot vacuums or smart thermostats learn your habits and operate automatically using AI.
Practical Use Cases
- Healthcare: AI can analyze medical images (like X-rays) to help doctors find problems. It also helps in diagnosing diseases and suggesting treatments.
- Finance and Banking: Banks use AI to detect fraud (unusual transactions) and to advise on investments. AI also helps in approving loans by assessing information quickly.
- Retail and E-commerce: Online stores use AI to recommend products you might like. It also helps in managing inventory, pricing, and customer service.
- Manufacturing and Automation: Robots powered by AI can assemble products in factories. AI also predicts when machines need maintenance before they break.
- Transportation and Self-driving Cars: AI helps cars drive themselves by recognizing roads, signs, and obstacles. It also improves traffic flow and public transport schedules.
- Education: AI can personalize learning for students. For example, educational software can adjust difficulty based on a student’s performance and give feedback.
- Agriculture: Farmers use AI for monitoring crops (using drones and sensors) and to decide when to water or harvest, increasing yield.
- Entertainment: Video games use AI to control characters (non-player characters) so they can make smart moves or react to the player. Movie studios use AI in animation and special effects.
- Customer Service: Chatbots and virtual assistants on websites help answer customer queries quickly, using natural language understanding.
- Environmental Science: AI helps predict weather patterns, analyze climate data, and aid in conservation efforts by identifying species in images.
Exam Focus
- AI (Artificial Intelligence): Simulation of human intelligence by machines (like learning, reasoning).
- Machine Learning: A subfield of AI where computers improve by learning from data (examples).
- Common Exam Questions:
- What is Artificial Intelligence?
- How is machine learning related to AI?
- Give an example of AI in daily life.
- Key Points to Memorize: Computers need data and algorithms; AI includes ML and possibly deep learning; it imitates human tasks.
- Differences:
- AI vs ML: AI is the broad field of intelligent machines, while ML is a way to achieve AI using data.
- Narrow vs General AI: Narrow AI performs specific tasks (like a calculator), General AI would perform any intellectual task a human can (not yet real).
Common Misconceptions
- AI is like a human brain: Many people think AI machines “think” or “understand” like humans. Actually, AI does not have feelings or consciousness. It follows patterns in data. It can appear smart, but it does not truly “know” things; it just processes information according to its programming.
- AI can solve any problem: People may believe AI is a magic solution. In reality, AI works only for tasks it is trained for, and its decisions are based on the data it has seen. It cannot understand or decide things outside its training.
- AI is always correct: Beginners often assume AI results are always right. However, AI can make mistakes, especially if the data was biased or incomplete. For example, an AI might misclassify an image if it has not seen enough examples of that kind.
- AI will replace all jobs: There’s a fear that AI will take every human job. While AI automates some tasks, it also creates new kinds of jobs and tools. People will still be needed to design, maintain, and work with AI systems. It often makes human work easier rather than entirely replacing it.
- Only experts can use AI: Some think AI is too complex to learn. While advanced AI requires deep study, beginners can start with simple concepts. There are many user-friendly resources to learn basic AI without being an expert.
Advantages & Limitations
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Automates repetitive tasks | Requires large amounts of data |
| Works faster than humans | Lacks human common sense and creativity |
| Learns and improves over time | Can be biased if trained on biased data |
| Available 24/7 without fatigue | Can make mistakes or be overconfident |
| Can discover patterns humans miss | Developing AI systems can be complex |
Beginner Learning Path
- Start with Computer Basics: Begin by understanding how computers work and learning basic programming logic. You can use simple coding (like block-based coding or an easy language) to get comfortable with writing instructions.
- Learn Basic Mathematics: Refresh arithmetic, algebra, and basic statistics or probability. These math concepts help in understanding how data is processed and how AI algorithms work.
- Understand Data: Learn what data is and how to handle it. Work with simple data sets (for example, in spreadsheets) to see patterns. Practice sorting data or finding simple trends.
- Study AI Concepts: Take beginner-friendly courses, videos, or books about AI and machine learning. Focus on understanding the ideas (like what an algorithm or model is) more than the complex math at first.
- Hands-on Practice: Try small projects or tutorials. For example, write a program to identify handwritten digits or sort text into categories. There are examples you can run on your computer or in free online tools.
- Join Communities: Participate in study groups or online forums. Discussing with peers or mentors can help you solve problems and stay motivated.
- Keep Learning: As you get comfortable, explore more advanced topics like neural networks. Work on bigger projects like creating a simple chatbot or image recognizer. Practice regularly and build a portfolio of what you learn.
Future Scope
- Career Opportunities: AI is one of the fastest-growing fields in technology. Many companies look for people who understand AI. Jobs like AI Engineer, Data Scientist, or Machine Learning Engineer are in high demand and often come with good salaries.
- Industry Growth: Almost every industry (healthcare, finance, manufacturing, entertainment, etc.) uses AI to improve products and services. This means learning AI concepts can open doors in many sectors.
- Innovation and Research: AI is at the heart of future tech like self-driving cars, smart robots, and virtual reality. By understanding AI, students can be part of cutting-edge projects that shape the future.
- Interdisciplinary Impact: AI connects with other fields such as mathematics, biology, or design. For example, AI helps doctors diagnose diseases or artists create generative art. Knowing AI principles can benefit careers even outside computer science.
- Lifelong Learning: AI technology keeps evolving. By starting with the basics now, students prepare themselves for new developments and technologies that will use AI in the future.
Summary
- AI Defined: Artificial Intelligence is the technology that allows machines to perform tasks like learning, reasoning, and problem-solving, similar to human intelligence.
- How It Works: AI systems learn from large amounts of data using algorithms. They build a model from examples and use it to make predictions or decisions on new data.
- Everyday Impact: We encounter AI in daily life through voice assistants, search engines, recommendation services, and many other applications. AI is also used in industries like healthcare, finance, and transportation.
- Key Points: Remember the basic terms (like AI and Machine Learning) and how they relate. AI usually refers to all intelligent computer systems, while machine learning is one way to achieve AI.
- Future Skills: As AI continues to grow, understanding these fundamentals is very useful. It can help you with exams and give you a strong start in technology and AI careers.
In short, AI is about teaching computers to be smart using data and algorithms. It’s an exciting and important field for today’s students and the future of work.